publications
My research interest is broadly in computer vision, machine learning and robotics, with a focus on 3D Computer Vision, Generative Model and Robot Learning.
2025
- ICCV
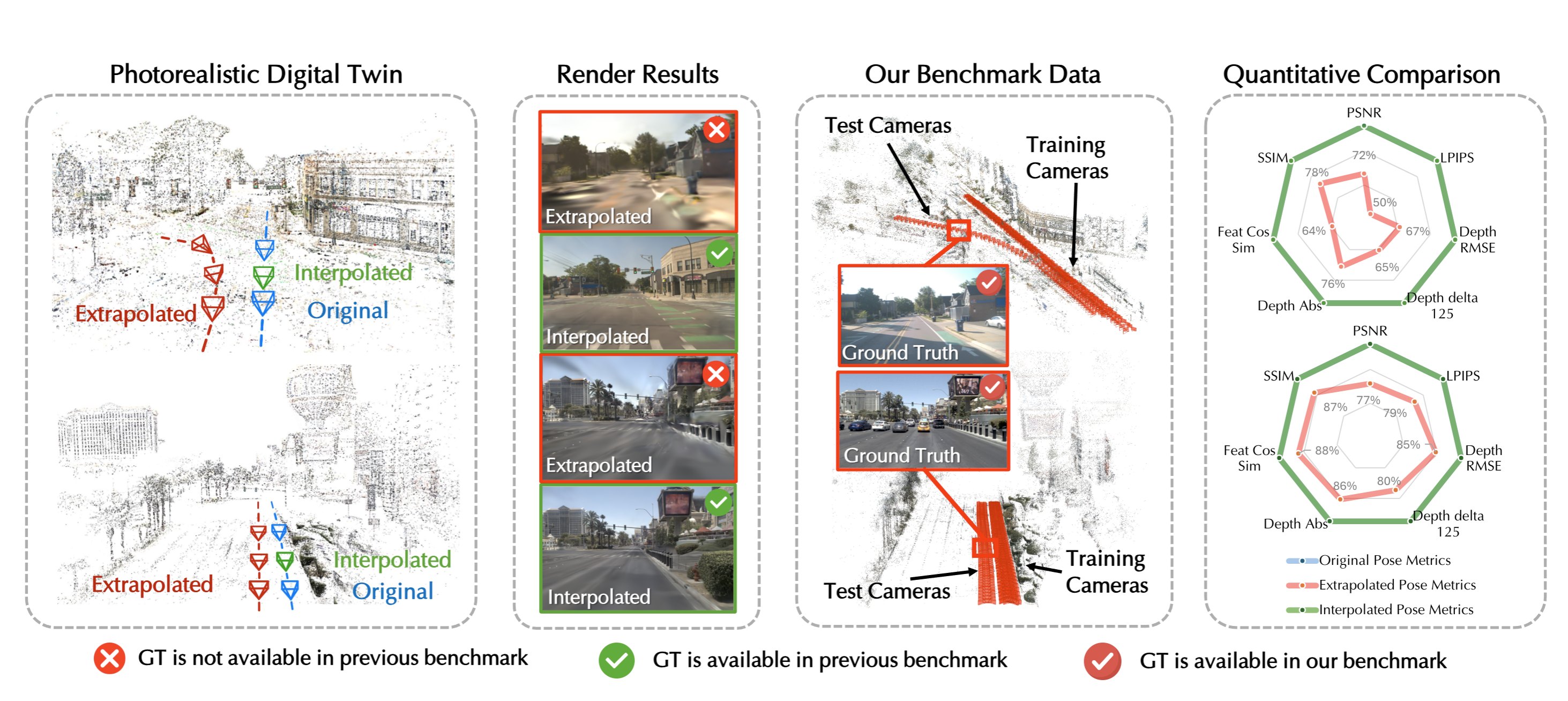 Extrapolated Urban View Synthesis BenchmarkXiangyu Han, Zhen Jia, Boyi Li, and 8 more authorsIEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2025
Extrapolated Urban View Synthesis BenchmarkXiangyu Han, Zhen Jia, Boyi Li, and 8 more authorsIEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2025Photorealistic simulators are essential for the training and evaluation of vision-centric autonomous vehicles (AVs). At their core is Novel View Synthesis (NVS), a crucial capability that generates diverse unseen viewpoints to accommodate the broad and continuous pose distribution of AVs. Recent advances in radiance fields, such as 3D Gaussian Splatting, achieve photorealistic rendering at real-time speeds and have been widely used in modeling large-scale driving scenes. However, their performance is commonly evaluated using an interpolated setup with highly correlated training and test views. In contrast, extrapolation, where test views largely deviate from training views, remains underexplored, limiting progress in generalizable simulation technology. To address this gap, we leverage publicly available AV datasets with multiple traversals, multiple vehicles, and multiple cameras to build the first Extrapolated Urban View Synthesis (EUVS) benchmark. Meanwhile, we conduct quantitative and qualitative evaluations of state-of-the-art Gaussian Splatting methods across different difficulty levels. Our results show that Gaussian Splatting is prone to overfitting to training views. Besides, incorporating diffusion priors and improving geometry cannot fundamentally improve NVS under large view changes, highlighting the need for more robust approaches and large-scale training. We have released our data to help advance self-driving and urban robotics simulation technology.
- Preprint
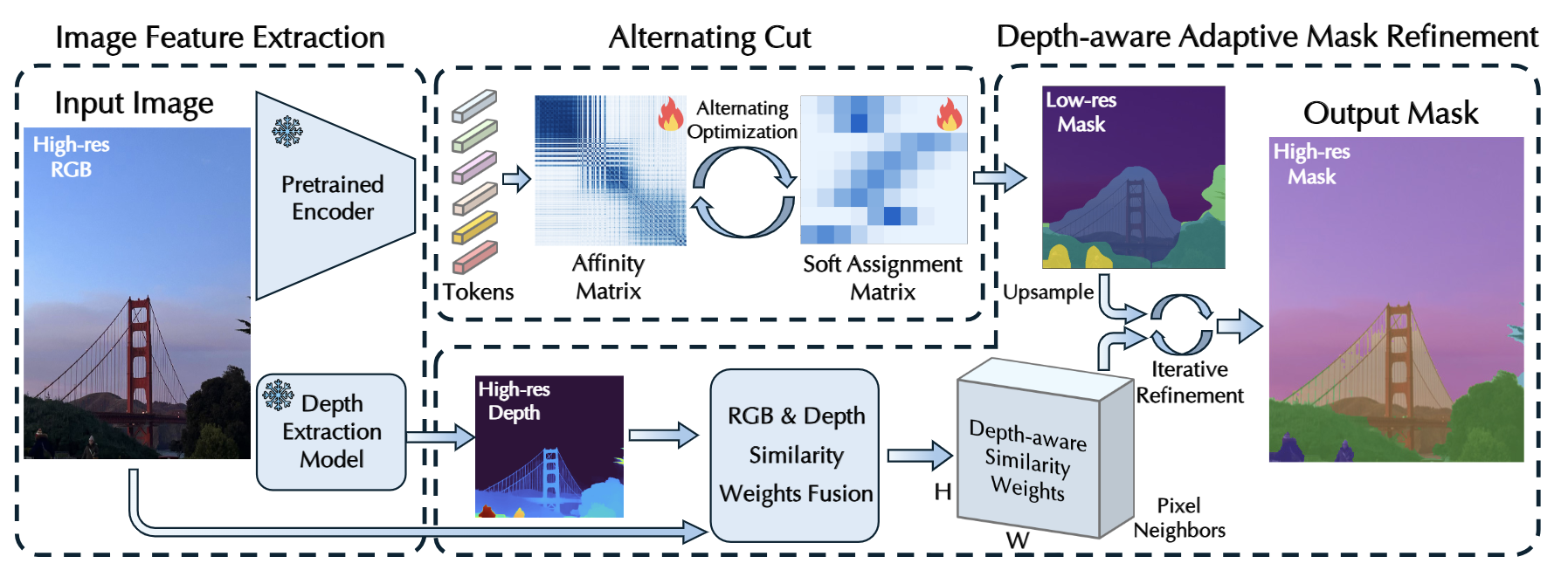 Falcon: Fractional Alternating Cut with Overcoming minima in Unsupervised SegmentationXiao Zhang, Xiangyu Han, Xiwen Lai, and 3 more authorsUnder Review, 2025
Falcon: Fractional Alternating Cut with Overcoming minima in Unsupervised SegmentationXiao Zhang, Xiangyu Han, Xiwen Lai, and 3 more authorsUnder Review, 2025Today’s unsupervised image segmentation algorithms often segment suboptimally. Modern graph-cut based approaches rely on high-dimensional attention maps from Transformer-based foundation models, typically employing a relaxed Normalized Cut solved recursively via the Fiedler vector (the eigenvector of the second smallest eigenvalue). Consequently, they still lag behind supervised methods in both mask generation speed and segmentation accuracy. We present a regularized fractional alternating cut (Falcon), an optimization-based K-way Normalized Cut without relying on recursive eigenvector computations, achieving substantially improved speed and accuracy. Falcon operates in two stages: (1) a fast K-way Normalized Cut solved by extending into a fractional quadratic transformation, with an alternating iterative procedure and regularization to avoid local minima; and (2) refinement of the resulting masks using complementary low-level information, producing high-quality pixel-level segmentations. Experiments show that Falcon not only surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods by an average of 2.5% across six widely recognized benchmarks (reaching up to 4.3% improvement on Cityscapes), but also reduces runtime by around 30% compared to prior graph-based approaches. These findings demonstrate that the semantic information within foundation-model attention can be effectively harnessed by a highly parallelizable graph cut framework. Consequently, Falcon can narrow the gap between unsupervised and supervised segmentation, enhancing scalability in real-world applications and paving the way for dense prediction-based vision pre-training in various downstream tasks.
2022
- Automotive Innovation
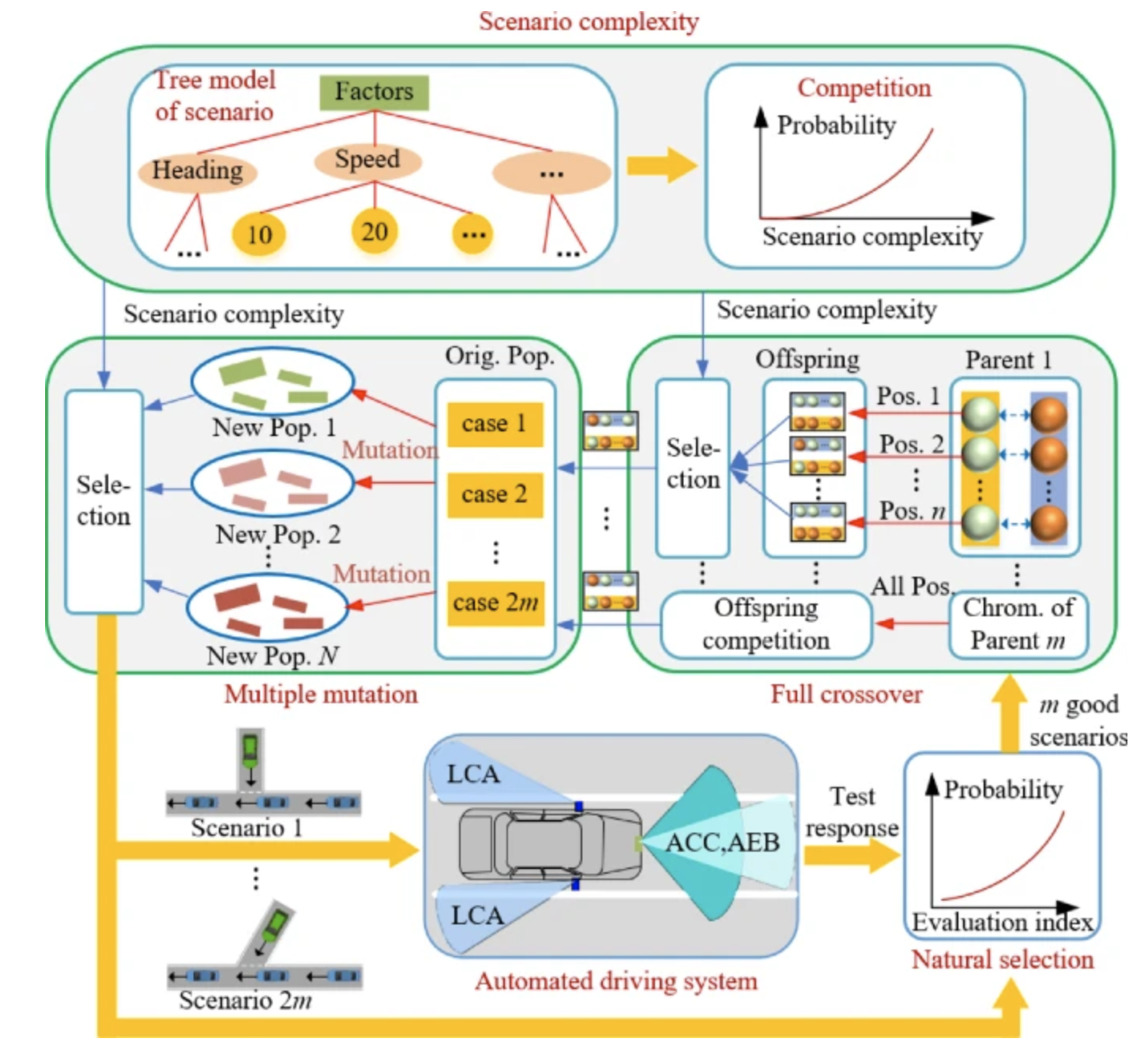 Performance Limit Evaluation Strategy for Automated Driving SystemsFeng Gao, Jianwei Mu, Xiangyu Han, and 2 more authorsAutomotive Innovation, 2022
Performance Limit Evaluation Strategy for Automated Driving SystemsFeng Gao, Jianwei Mu, Xiangyu Han, and 2 more authorsAutomotive Innovation, 2022Efficient detection of performance limits is critical to autonomous driving. As autonomous driving is difficult to be realized under complicated scenarios, an improved genetic algorithm-based evolution test is proposed to accelerate the evaluation of performance limits. It conducts crossover operation at all positions and mutation several times to make the high-quality chromosome exist in candidate offspring easily. Then the normal offspring is selected statistically based on the scenario complexity, which is designed to measure the difficulty of realizing autonomous driving through the Analytic Hierarchy Process. The benefits of modified cross/mutation operators on the improvement of scenario complexity are analyzed theoretically. Finally, the effectiveness of improved genetic algorithm-based evolution test is validated after being applied to evaluate the collision avoidance performance of an automatic parallel parking system.
2021
- Electronics
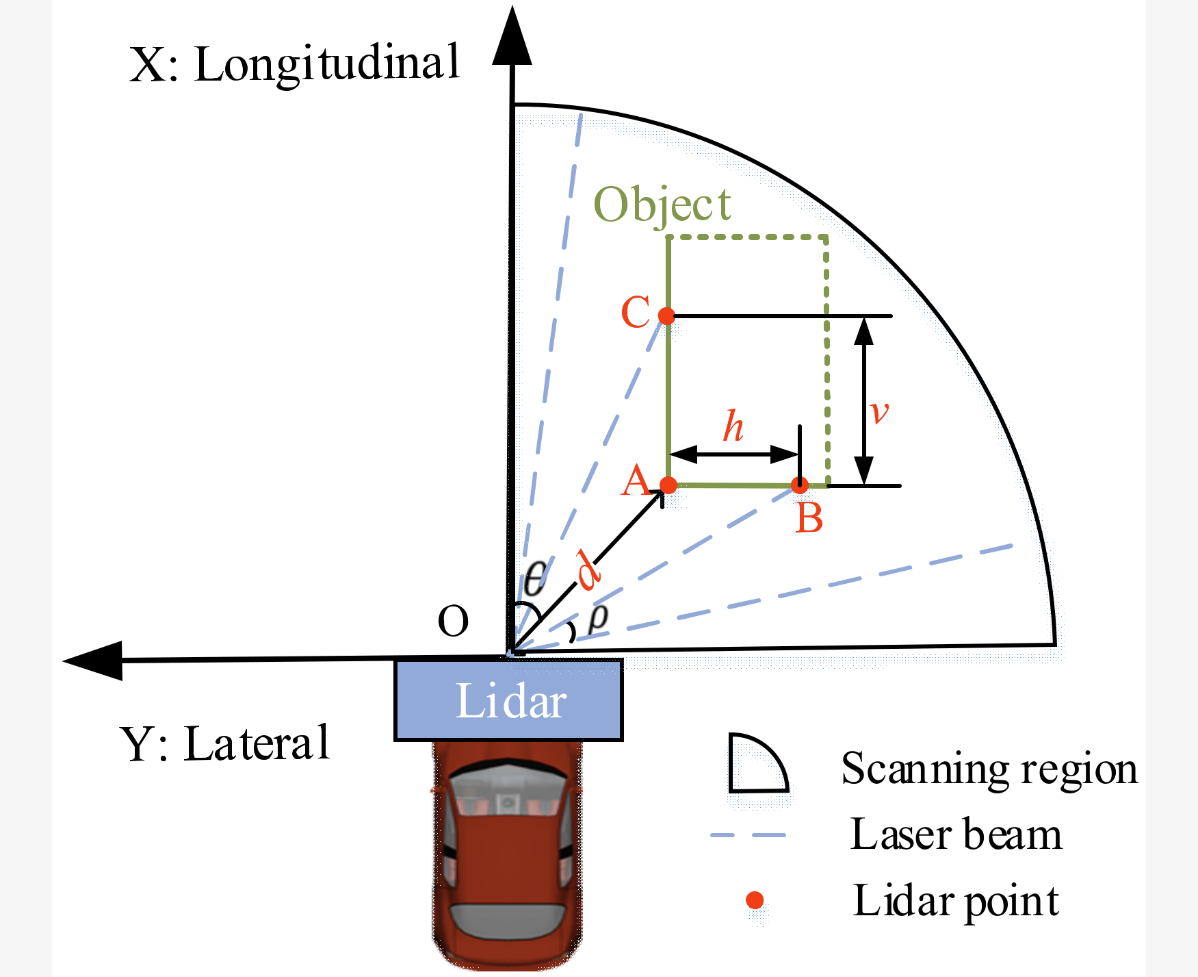 A new density-based clustering method considering spatial distribution of lidar point cloud for object detection of autonomous drivingCaihong Li, Feng Gao, Xiangyu Han, and 1 more authorElectronics, 2021
A new density-based clustering method considering spatial distribution of lidar point cloud for object detection of autonomous drivingCaihong Li, Feng Gao, Xiangyu Han, and 1 more authorElectronics, 2021Lidar is a key sensor of autonomous driving systems, but the spatial distribution of its point cloud is uneven because of its scanning mechanism, which greatly degrades the clustering performance of the traditional density-based spatial clustering of application with noise (DSC). Considering the outline feature of detected objects for intelligent vehicles, a DSC-based adaptive clustering method (DAC) is proposed with the adoption of an elliptic neighborhood, which is designed according to the distribution properties of the point cloud. The parameters of the ellipse are adaptively adjusted with the location of the sample point to deal with the uniformity of points in different ranges. Furthermore, the dependence among different parameters of DAC is analyzed, and the parameters are numerically optimized with the KITTI dataset by considering comprehensive performance. To verify the effectiveness, a comparative experiment was conducted with a vehicle equipped with three IBEO LUX8 lidars on campus, and the results show that compared with DSC using a circular neighborhood, DAC has a better clustering performance and can notably reduce the rate of over-segmentation and under-segmentation.
- Applied Sciences
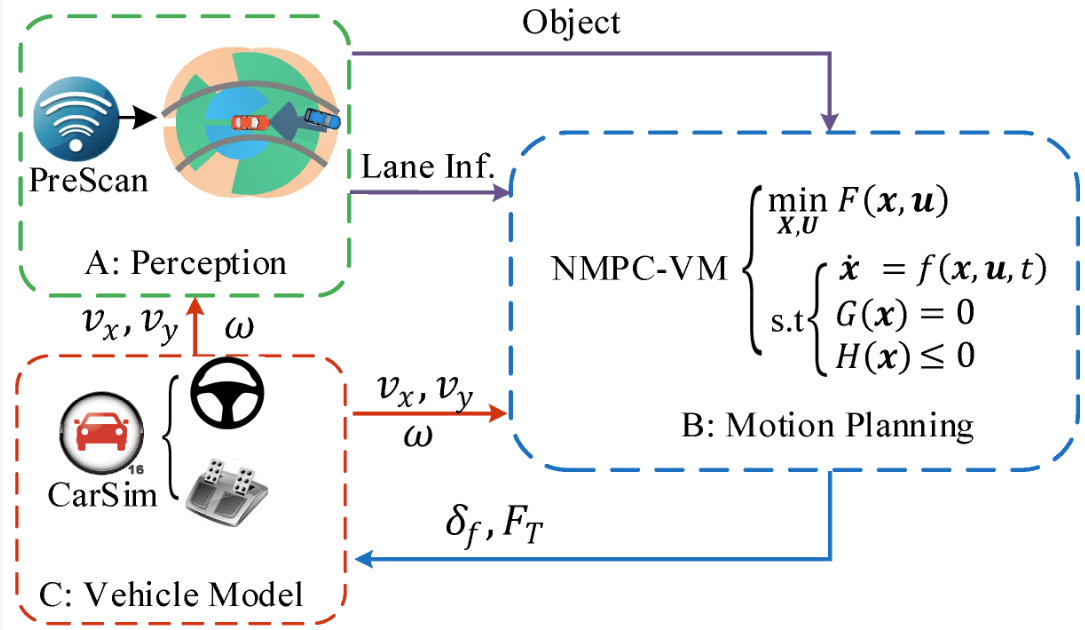 A simplified vehicle dynamics model for motion planner designed by nonlinear model predictive controlFeng Gao, Qiuxia Hu, Jie Ma, and 1 more authorApplied Sciences, 2021
A simplified vehicle dynamics model for motion planner designed by nonlinear model predictive controlFeng Gao, Qiuxia Hu, Jie Ma, and 1 more authorApplied Sciences, 2021Motion planning by considering it as an optimal problem is an effective and widely applicable method. Its comprehensive performance greatly depends on the vehicle dynamics model, which is highly coupled and nonlinear, especially under the dynamical scenarios and causes much more consumption of computation resources for the numerical optimization. To increase the real time performance of the motion planner designed by nonlinear model predictive control (NMPC), a unified and simplified vehicle dynamics model (SDM) is presented to make a balance between the accuracy and complexity for dynamical driving scenarios. Based on the statistical analysis results of naturalistic driving conditions, a unified nonlinear vehicle dynamics model is set up, which considers the tyre cornering characteristic and is also applicable to conditions with large turning angle. After the validation of this coupled dynamics model (CDM) by comparisons with other widely used models under a variety of conditions, the coupling effect is analyzed according to the transfer functions, which are obtained by linearizing CDM at equilibrium points. Furthermore, SDM is derived by ignoring the weak part of the coupling effect. The accuracy of SDM is validated by several comparative studies with other models and it is further applied to design a motion planner by NMPC to validate its contribution on the performance improvement under dynamical driving conditions.